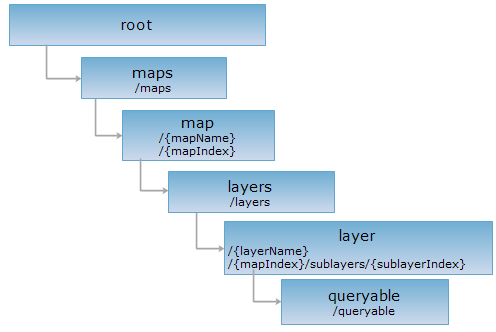
<layer_uri>/queryable[.<format>]
As a child resource of the layer, the queryable resource is used to identify whether or not the layer can be used for query. By performing a PUT request on the queryable resource, it can change the query state of the layer.
Supported methods
Supported output formats: rjson, json, html, xml.

Here is an example of performing an HTTP request on the following URI, with rjson as the output format. In the URI, supermapiserver is the name of the server, "WorldMap" is the map name (mapName), Capitals@World is a layer of Map "WorldMap" (layerName), Capitals@World@@WorldMap represents a sublayer of World layer. Therefore, the URI represents the queryable resource of the Capitals@World layer.
http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/map-world/rest/maps/WorldMap/layers/Capitals@World@@WorldMap/queryable.rjson
Gets the description of the layer visibility. Returning true: visible, false: invisible.
| Field | Type | Definition |
| _cache | boolean | [Optional parameters] Whether to use cache, the default is True. False means close all the caches. |
A GET request is performed on the queryable resource, and a Boolean value is returned, indicating whether or not the layer can be queried. True indicates query.
A GET request is performed on the following queryable resource: http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/map-world/rest/maps/WorldMap/layers/Capitals@World@@WorldMap/queryable.rjson, and the query message of Capitals@World can be returned, shown as follows:
true
Ask for the response identical to the one that would correspond to a GET request, but without the response body. This is useful for retrieving meta-information written in response headers, without having to transport the entire content. The meta-information includes the media-type, content-encoding, transfer-encoding, content-length, etc.
The HEAD request helps check the existence of the querable resource and whether it can be accessed by the client. By implementing the HEAD request on the URI, with .<format> appended to the end, we can quickly get to know whether queryable resource supports the representation in <format> or not.