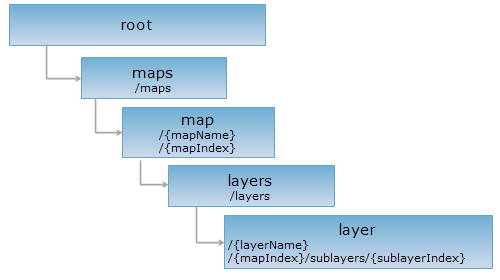
1. <layers_uri>/{layerName}[.<format>]
2. <layers_uri>/{layerIndex}[.<format>]
3. <layers_uri>/{layerIndex}/sublayers/{sublayerIndex}[.<format>]
legend, visible, queryable, style
The layer resource represents a layer, identified by layerName or layerIndex in URI. You can access a layer resource with the above 3 ways.
A layer resource can be a higher level layer like UGCMapLayer (SuperMap map layer), WFSLayer, WMSLayer, etc., or a lower level layer like the sublayer of the UGCMapLayer, such as a UGCVectorLayer, UGCGridLayer, UGCImageLayer, UGCThemeLayer, etc. A higher level layer is identified by the type field and a lower level layer is identified by the ugcLayerType field.
When the layer resource is a higher level layer, it can be accessed with URI1 or URI2. When the layer resource is a lower level layer, it can be accessed with URI1 or URI3.
{layerName} is used to identify the name of a higher or lower level layer. {layerName} is used to identify the index of a higher level layer, starting from 0. {sublayerIndex} is used to identify a lower level layer, starting from 0 and increasing by order in the layer list For example, the index number of the first layer is 0, the index number of the second layer is 1, and so on..
Please refer to Get sublayer list for information about this resource usage.
Supported Methods:
Supported output formats: RJSON, JSON, HTML, XML.
Here is an example of performing an HTTP request on the following URI, with rjson as the output format. In the URI, supermapiserver is the name of the server, "World Map" is the map name {mapName}, Capitals@World is a layer of Map "World Map" ({layerName}), Capitals@World@@ World Map represents a sublayer of World Map layer. URI represents the Capitals@World layer, a layer resource.
http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/map-world/rest/maps/World Map/layers/Capitals@World@@World Map.rjson
By performing a GET request on the example URI, the representation of Capitals@World layer in "World Map" can be got.
| Name | Type | Description |
| _cache | boolean | [Optional] Whether to use cache, the default is True. False means close all the caches. |
The returned resource representation represents various information of the layer, and there is difference in description of various types of layers. The layers may be the higher layers: UGCMapLayer, WFSLayer, and WMSLayer,etc., or lower layers: sublayers (UGCVectorLayer, UGCGridLayer, UGCImageLayer, UGCThemeLayer) of WFSLayer, WMSLayer, and UGCMapLayer, etc. The structure of the layer resource representation is identical to the descriptions of these layers.
The example layer Capitals@World is a UGCVectorLayer, so the returned representation is the structure of UGCVectorLayer, shown as follows:
| Name | Type | Description |
| name | String | The layer name. The layer name is the only identifier of this layer in the map. The identifier is not case-sensitive. |
| bounds | double | The layer extent. |
| caption | String |
The layer title. The default is that it is consistent with name. In the legend and layer control list, the layer name is the value of caption. Note: Distinguish with name. |
| description | String | The description information of the layer. |
| queryable | boolean | Whether or not the objects of the layer can be queried. True indicates the object can be queried, while false indicates the objects can not be queried. |
| visible | boolean | The layer visibility. When the layer is not visible, the setting of all the other attributes will be invalid. |
| type | LayerType | The type of this layer. Currently supported layers include: UGC (SuperMap Layer), WFS (WFS Layer), WMS (WMS Layer) and CUSTOM (Custom Layer). |
| subLayers | Layer[] | The sublayers set. |
| completeLineSymbolDisplayed | boolean | Whether to display the complete line symbol. True indicates display, while false indicates not display. |
| maxScale | double | The layer maximum visible scale. The maximum visible scale can not be negative. If the current display scale of the map is larger than its maximum visible scale, the layer will not be displayed. The default is 0. |
| minScale | double | The minimum visible scale of this Layer. The minimum visible scale of a layer should not be negative. When current display scale of the map is less than the minimum visible scale of this layer, this layer will not be displayed. The default is 0. |
| minVisibleGeometrySize | double | The minimum visible size of geometry object. Unit: Pixels |
| opaqueRate | int | The layer opacity, 0-100. |
| symbolScalable | boolean | Whether or not the symbol size of layer zooms with the map image. True indicates the symbol zooms in or out when the image zooms in or out; false indicates the symbol does not zoom in or out when the image zooms in or out. |
| symbolScale | double | The reference scale for scaling symbols. The zoom reference scale of layer symbols. The reference scale of the symbol is valid when symbols are set to zoom with the map. The reference scale designates the display scale of the map when the symbol is at the specified symbol size. |
| datasetInfo | DatasetInfo | The dataset object corresponded to layer. The layer is the reference of dataset. Therefore, one layer corresponds to one dataset. |
| displayFilter | String | The layer display filter condition. The filter condition is the filter of attribute data of the database. For example, there is smid field in the layer attribute, and the filter condition is smid >20, so the geometry objects with the value of smid larger than 20, will be displayed in the map window. While the rest of objects do not display. |
| joinItems | JoinItem[] | The join items information. |
| representationField | String | The field storing the representation information. Representation is the presentation of information associated with geometric objects in vector datasets. With representation, geometric objects can be displayed in different styles, with the original geometric objects undisplayed and unchanged. |
| ugcLayerType | UGCLayerType | Type of SuperMap layer. The SuperMap layer type. The types of SuperMap layer include: GRID, IMAGE, THEME, VECTOR, WFS (WFSLayer) and WMS. |
| style | Style | The vector layer style. |
Here is an example of performing a GET request on Capitals@World resource, and the information contained in Capitals@World layer is returned (Capitals@World is a UGCVectoerLayer) in rjson output format:
{
"bounds": {
"bottom": -41.21039581298828,
"left": -99.12757110595705,
"leftBottom": {
"x": -99.12757110595705,
"y": -41.21039581298828
},
"right": 175.14494323730466,
"rightTop": {
"x": 175.14494323730466,
"y": 64.31326293945314
},
"top": 64.31326293945314
},
"caption": "Capitals@World",
"completeLineSymbolDisplayed": false,
"datasetInfo": {
"bounds": {
"bottom": -41.21039581298828,
"left": -99.12757110595705,
"leftBottom": {
"x": -99.12757110595705,
"y": -41.21039581298828
},
"right": 175.14494323730466,
"rightTop": {
"x": 175.14494323730466,
"y": 64.31326293945314
},
"top": 64.31326293945314
},
"dataSourceName": "World",
"description": null,
"encodeType": null,
"isReadOnly": false,
"name": "Capitals",
"prjCoordSys": null,
"tableName": null,
"type": "POINT"
},
"description": "",
"displayFilter": "",
"joinItems": null,
"maxScale": 0,
"minScale": 7.56550553E-8,
"minVisibleGeometrySize": 0.4,
"name": "Capitals@World",
"opaqueRate": 100,
"queryable": true,
"representationField": "",
"style": {
"fillBackColor": {
"blue": 255,
"green": 255,
"red": 255
},
"fillBackOpaque": true,
"fillForeColor": {
"blue": 196,
"green": 196,
"red": 196
},
"fillGradientAngle": 0,
"fillGradientMode": "NONE",
"fillGradientOffsetRatioX": 0,
"fillGradientOffsetRatioY": 0,
"fillOpaqueRate": 100,
"fillSymbolID": 0,
"lineColor": {
"blue": 0,
"green": 0,
"red": 0
},
"lineSymbolID": 0,
"lineWidth": 0.1,
"markerAngle": 0,
"markerSize": 2,
"markerSymbolID": 12
},
"subLayers": {},
"symbolScalable": false,
"symbolScale": 0,
"type": "UGC",
"ugcLayerType": "VECTOR",
"visible": true
}
Returns the same HTTP response header as the GET request, but no response entity, which can be used to retrieve the meta data contained in response message header without having to transmit the entire response content. Meta data information includes media type, character coding, compression coding, entity content length, etc.
HEAD request is used to determine whether the layer resource exists, or if the user has the authority to access it. By executing an HEAD request with a .<format> URI, you can quickly determine whether the layer resource supports the <format> representation.