A datasource resource represents a datasource. The datasource resource provides the datasource information and entries for accessing its datasets. You can modify the datasource information by implementing the PUT request on the datasource resource. The information about the datasource you can get through the datasource resource includes: the datasource name, dataset description, engine type, distance unit, coordinate unit, projection, etc. The information that can be modified includes: the dataset description, distance unit, coordinate unit, etc.
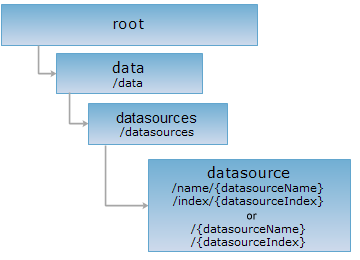
The datasource resource can be identified with 4 ways of URIs. URI1 identifies a datasource with /name/{datasourceName}, i.e., the "/name" tag and the datasource name. URI2 identifies a datasource with /index/{datasourceIndex}, i.e., the /index tag and the datasoruce index. URI3 identifies a datasource with /{datasourceName}, i.e., the datasource name. URI4 identifies a datasource with /{datasourceIndex}, i.e., the datasource index. datasourceName is used to identify a datasource resource with a higher priority.
Supported methods:
Supported output formats: rjson, json, html, xml.
Implement the HTTP request on the following URI, where supermapiserver is the server name and World is a datasource on the server, and get the response in rjson format.
http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/data-world/rest/data/datasources/name/World.rjson
Gets the datasource information and the dataset information list.
None.
When implementing the GET request on the datasource resource, the representation of the resource returned is included in the entity body of the response message, as shown below:
| Field | Type | Description |
| datasourceInfo | DatasourceInfo | Includes the information such as the datasource name, datasource description, engine type, projection, unit, etc. |
| childUriList | List<String> | Child resources, that is, the URI list for datasets in the datasource. |
The datasourceInfo field describes the datasource information. Please see the introduction to the DatasourceInfo type in javadoc to know the structure of datasourceInfo. For your convenience, the structure list of the datasourceInfo field is listed below.
| Field | Type | Description |
| coordUnit | Unit | The unit for the coordinates. |
| description | String | The description of the datasource. |
| distanceUnit | Unit | The distance unit. |
| engineType | EngineType | The engine type of the datasource. Readonly. |
| name | String | The alias of the datasource. Used to uniquely identify a datasource in the workspace. Readonly. |
| containDatasetGroup | boolean | Whether to include a data set group. |
| supportTransaction | boolean | Whether the current data source supports database transaction capability of rolling back transactions. Only the PostGIS data sources in the workspace are suppoeted, so the parameter value is true, otherwhise the value is false. |
| prjCoordSys | PrjCoordSys | The projection. |
Implement the GET request on the datasource resource with http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/data-world/rest/data/datasources/name/World.rjson to get the response in rjson format, as shown below:
{
"childUriList": ["http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/data-world/rest/data/datasources/name/World/datasets"],
"datasourceInfo": {
"coordUnit": "DEGREE",
"description": "",
"distanceUnit": "METER",
"engineType": "UDB",
"name": "World",
"prjCoordSys": {
"coordSystem": {
"datum": {
"name": "D_WGS_1984",
"spheroid": {
"axis": 6378137,
"flatten": 0.0033528107,
"name": "WGS_1984",
"type": "SPHEROID_WGS_1984"
},
"type": "DATUM_WGS_1984"
},
"name": "GCS_WGS_1984",
"primeMeridian": {
"longitudeValue": 0,
"name": "Greenwich",
"type": "PRIMEMERIDIAN_GREENWICH"
},
"spatialRefType": "SPATIALREF_EARTH_LONGITUDE_LATITUDE",
"type": "GCS_WGS_1984",
"unit": "DEGREE"
},
"coordUnit": "DEGREE",
"distanceUnit": "METER",
"epsgCode": 1,
"name": "Longitude / Latitude Coordinate System---GCS_WGS_1984",
"projection": null,
"projectionParam": null,
"type": "PCS_EARTH_LONGITUDE_LATITUDE"
}
}
}
Modifies the datasource information.
The parameters contained in the request body to modify or datasource information when implementing the PUT request on the datasource resource are as follows:
| Name | Type | Description |
| description | String | The descriptive information for the datasource. |
| coordUnit | Unit | The unit for the coordinates. |
| distanceUnit | Unit | The distance unit. |
When implementing the PUT request on the datasource resource, the representation of the resource returned is included in the entity body of the response message, as shown below:
| Field | Type | Description |
| succeed | boolean | Whether the modify operation on the datasource information is successful. |
| error | HttpError | Error message. If successful, the field will not exist. |
Parameters need for implementing the PUT request on the example datasource resource with http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/data-world/rest/data/datasources/name/World.rjson are as follows:
{"coordUnit":"MILE","description":"This is a new description","distanceUnit":"MILE"}
If successful, the response in rjson format is as follows:
{"succeed": true}
Asks for the response identical to the one that would correspond to a GET request, but without the response body. This is useful for retrieving meta-information written in response headers, without having to transport the entire content. The meta-information includes the media-type, content-encoding, transfer-encoding, content-length, etc.
The HEAD request helps check the existence of the datasource resource and whether it can be accessed by the client. By implementing the HEAD request on the URI, with .<format> appended to the end, we can quickly get to know whether the datasource resource supports the representation in <format> or not.