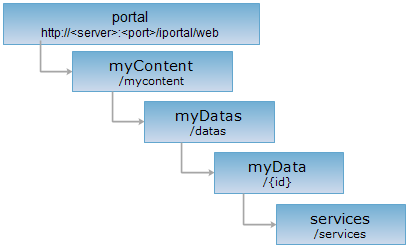
<myData_uri>/services[.<format>]
The services resource is used to obtain the published service information for the uploaded data.
Supported Methods:
Supported output formats: rjson, json, html, xml.

Implement the HTTP request on the following URI, where supermapiportal is the server name, with rjson being the output format.
http://supermapiportal:8090/iportal/web/mycontent/datas/{id}/services.rjson
Obtains the published service information for the uploaded data.
The structure of the response resource representation is as follows:
| Field | Type | Description |
| dataID | Integer | ID of the data. |
| serviceID | String | ID of the service. |
| serviceNode | String | The ID of the server node. |
| serviceName | String | The service alias. |
| serviceStatus | ServiceStatus | The publishing state, including: UNPUBLISHED (unpublished), PUBLISHING (being publishing), PUBLISHED (published), PUBLISH_FAILED (fail to publish), DOES_NOT_INVOLVE (can't be published), UNPUBLISHED_FAILED (fail to cancel the publishing). |
| serviceType | DataServiceType | The type of service that is currently supported includes RESTDATA (data service), RESTMAP (map service), and RESTREALSPACE (3D service). |
| createTime | long | Service creating time. |
| updateTime | long | Service update time. |
| address | String | The service address, if the service agent is enabled, it will display the proxy service address. |
| accessCount | long | The number of times to access the service on that day the service is published. |
Implement the GET request on the services resource http://localhost:8090/iportal/web/mycontent/datas/9/services.rjson. Return rjson results:
[
{
"accessCount": 0,
"address": "http://192.168.120.40:8091/iserver/services/map_City/rest",
"createTime": null,
"dataID": 9,
"serviceID": "map_City",
"serviceName": null,
"serviceNode": "dz3l683h",
"serviceStatus": "PUBLISHED",
"serviceType": "RESTMAP",
"updateTime": null
}
]
Returns the same HTTP response header as the GET request, but does not have the response entity. It can get the metadata information in the response header without transferring the whole response content. Metadata information includes media type, character encoding, compression encoding, entity content length, and so on.
The HEAD request can be used to determine whether the services resource exists or whether the client has authority to access the resource. It can quickly determine whether the services resource supports the representation in <format> format by performing HEAD request on URI with <format>.